The 17 supplements you should know about to help slow aging!
The 17 supplements you should know about to help slow aging!
Aging | 04 Aug 2023
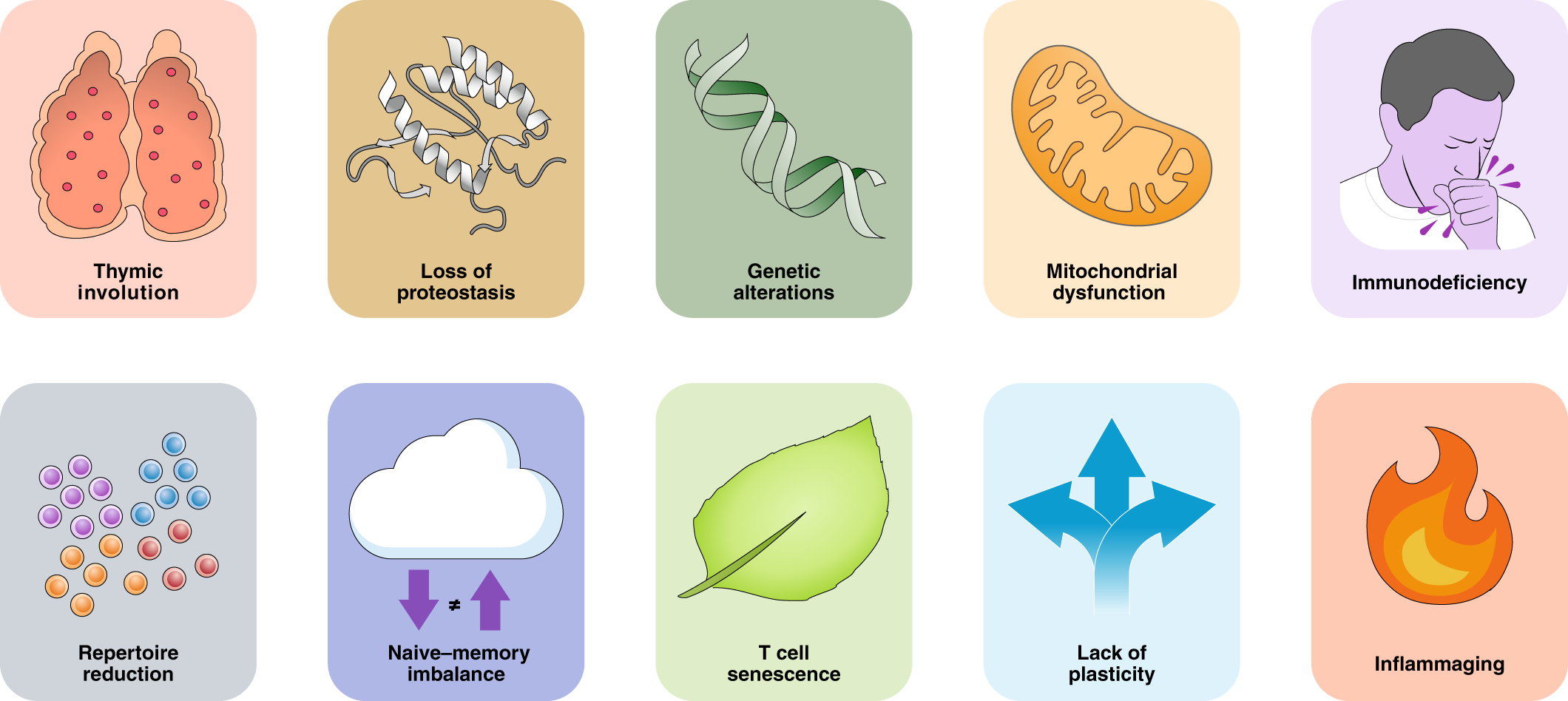
Here's how addition of the following supplements directly correlates with one or more of the 10 hallmarks of aging:
1. NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide):
- Mitochondrial dysfunction: NMN supports mitochondrial function and energy production, addressing age-related decline in mitochondrial health.
- Cellular senescence: NMN may help reduce the accumulation of senescent cells, promoting cellular rejuvenation.
2. Turmeric:
- Inflammation: Turmeric exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, reducing chronic inflammation associated with aging.
- Oxidative stress: Turmeric acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress.
3. Vitamin C:
- DNA damage: Vitamin C helps protect DNA from damage caused by oxidative stress.
- Cellular senescence: Vitamin C may help delay cellular senescence and promote healthy cell function.
4. Vitamin D:
- Immune system decline: Vitamin D supports immune function, addressing age-related decline in immune response.
- Bone health: Vitamin D helps maintain bone density and reduces the risk of age-related bone loss.
5. Vitamin E:
- Oxidative stress: Vitamin E acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
- Skin aging: Vitamin E supports skin health, reducing the impact of environmental factors on skin aging.
6. Vitamin K2:
- Bone health: Vitamin K2 plays a crucial role in calcium metabolism, supporting bone health and reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
7. Ashwagandha:
- Stress response: Ashwagandha helps modulate the stress response, supporting resilience and reducing the impact of chronic stress on aging.
- Cognitive decline: Ashwagandha may have neuroprotective effects, potentially reducing age-related cognitive decline.
8. Omega-3:
- Inflammation: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties, reducing chronic inflammation associated with aging.
- Heart health: Omega-3 supports cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of age-related heart disease.
9. Rapamycin:
- Cellular senescence: Rapamycin inhibits the mTOR pathway, which plays a role in cellular senescence, potentially slowing down the aging process.
10. TMG (Trimethylglycine):
- Oxidative stress: TMG acts as a methyl donor, supporting the production of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that helps reduce oxidative stress.
- Inflammation: TMG has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, reducing chronic inflammation associated with aging.
11. Spermidine:
- Autophagy: Spermidine induces autophagy, promoting cellular recycling and rejuvenation.
- Cellular senescence: Spermidine may help inhibit cellular senescence and support healthy cell function.
12. Urolithin A:
- Mitochondrial dysfunction: Urolithin A activates mitophagy, improving mitochondrial function and addressing age-related mitochondrial dysfunction.
13. Quercetin:
- Inflammation: Quercetin exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, reducing chronic inflammation associated with aging.
- Oxidative stress: Quercetin acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
14. Hyaluronic Acid:
- Tissue regeneration: Hyaluronic acid plays a role in tissue repair and regeneration, contributing to overall tissue health.
- Skin aging: Hyaluronic acid supports skin hydration and elasticity, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
15. Alpha Ketoglutarate:
- Metabolic dysregulation: Alpha ketoglutarate supports cellular metabolism and energy production, addressing age-related metabolic dysregulation.
- Stem cell exhaustion:
Alpha ketoglutarate can support stem cell function, potentially delaying stem cell exhaustion.
16. N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC):
- Oxidative stress: NAC boosts glutathione levels, reducing oxidative stress and protecting cells from damage.
- Inflammation: NAC exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, modulating the immune response and reducing chronic inflammation.
17. BPC 157:
- Tissue repair: BPC 157 promotes tissue repair and healing, supporting recovery from injuries and age-related damage.
- Inflammation: BPC 157 reduces inflammation and supports gut and neurological health.
It's important to note that while these supplements have shown potential benefits, their effects on aging and health may vary among individuals, and proper dosage and individual considerations should be taken into account. It's recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen. Contact a functional medicine physician at Patel Health today!
Contact Us
Let’s Connect